Smooth Transitions: Zero Downtime Deployment for Next-Generation Core Banking Systems

In today's fast-paced banking industry, the ability to implement new versions of core banking systems without any disruptions is crucial. Financial institutions need to keep up with customer expectations, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements while ensuring continuous service availability. This challenge has led to the concept of zero downtime deployment, where upgrades, improvements, and new features are seamlessly integrated into the core banking system without causing any interruptions.
ZDD– what’s it?
Zero downtime deployment (ZDD) refers to the process of deploying new versions of a core banking system without causing any disruption to its ongoing operations. It allows financial institutions to introduce updates, improvements, and new features seamlessly while maintaining continuous service availability for customers.
In our company, we offer various capabilities and features that support zero downtime deployment. BOS's architecture is designed to ensure high availability and scalability, enabling financial institutions to implement new versions of their core banking systems smoothly. They leverage cloud-native technologies, microservices, and containerization to achieve this objective.
Rolling deployment
One of the key approaches used to implement zero downtime deployment is the concept of rolling updates (or rolling deployments) With this technique, new versions of BOS system are deployed incrementally, in small batches or segments, rather than all at once. By deploying updates in this manner, the risk of system failures or disruptions is minimized. If any issues are encountered during the deployment of a particular segment, it can be rolled back while ensuring the rest of the system remains operational.
"Despite the increasing demand for core banking system transformations, only around 30% of such transformations have successfully migrated ledgers and products to new systems, indicating the complexity involved”.
Source: McKinsey Digital
At INCAT, we provide comprehensive documentation and resources that guide financial institutions on how to achieve zero downtime deployment. By following these guidelines, financial institutions can mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transition to new versions of their core banking systems.
We also attach great importance to proper testing and monitoring during the implementation process. Thorough testing, including unit testing, integration testing, and performance testing, helps identify potential issues before they affect the live system. Continuous monitoring of the system during and after the deployment ensures early detection of any anomalies and allows for immediate remediation.
Benefits of Zero Downtime Deployment
![]() Uninterrupted Banking Services
Uninterrupted Banking Services
With ZDD, banks can update their systems, introduce new features, and fix bugs without causing disruptions to customer access or transaction processing. This ensures uninterrupted banking services, preventing any inconvenience or financial loss to customers.
![]() Seamless User Experience
Seamless User Experience
ZDD ensures a seamless user experience by eliminating any service disruptions or downtime during the deployment process. Customers can continue using the banking applications without any interruptions, accessing their accounts, making transactions, and utilizing various financial services offered by the bank.
![]() Continuous Availability
Continuous Availability
Core banking systems need to be available 24/7, as customers expect round-the-clock access to their financial services. ZDD enables continuous availability by allowing updates and changes to be deployed without affecting system uptime.
"Banks worldwide spend millions of dollars each year maintaining their core banking systems, which handle high transaction volumes and are expected to function without interruptions."
By following best practices and leveraging the resources provided by platforms like BOS financial institutions can successfully implement new versions of their core banking systems while ensuring continuous service availability for their customers.
BOS' provider with "Forbes Diamonds 2023 Award". INCAT joins the fastest growing companies in Poland.

On Tuesday, June 6, 2023, the "Forbes Diamonds 2023" Gala was held at the Haston City Hotel in Wrocław (Poland), organized by the Polish editorial office of Forbes. During the event, the fastest-growing Polish companies were awarded. One of the statuettes went to our company.
“Forbes Diamonds 2023” is an annual ranking of companies that have most effectively increased their value in the last three years. It is a confirmation of strength, as well as the ability to build brand value and quality on the market.
What is important, the accolade is not awarded by a subjective jury on the basis of unspecified criteria, but the list is compiled by analysts from Dun&Bradstreet on the basis of the Swiss method of company valuation, taking into account financial results and the value of assets of enterprises. Finally, the award is given to companies with the highest dynamics of value growth.
Our company received a statuette in the category “Small companies with sales revenues from PLN 5 to 50 million”. On behalf of the organization, the award was received by Piotr Hanusiak – the leader of the company.
The award from Forbes Polska is a accolade for the entire team, so we congratulate all our employees and wish them further success, which will be confirmed by similar titles. 🏆
A few photos from the gala can be seen below, and the full photo report can be found at the link.





Unlocking agility and scalability: exploring BOS’ microservices architecture

Microservices architecture has become a popular approach for developing complex software systems. The use of microservices enables organizations to create software systems that are scalable, resilient, and easy to maintain. Does microservice architecture also work in financial institutions? And how microservices can prove themselves in IT solutions for fintechs and neo-banks?
This is another article from the BOS Inside series, in which we present the architecture of our flexible core banking software.
What is MSA?
The microservices architecture, also known as microservices, involves developing computer applications as a collection of loosely coupled services that operate independently of each other. Each service performs a specific function and communicates with other services using lightweight communication protocols. Microservices are autonomous in their development, deployment and maintenance, meaning that they can be developed independently of the rest of the system.
Microservices in core banking
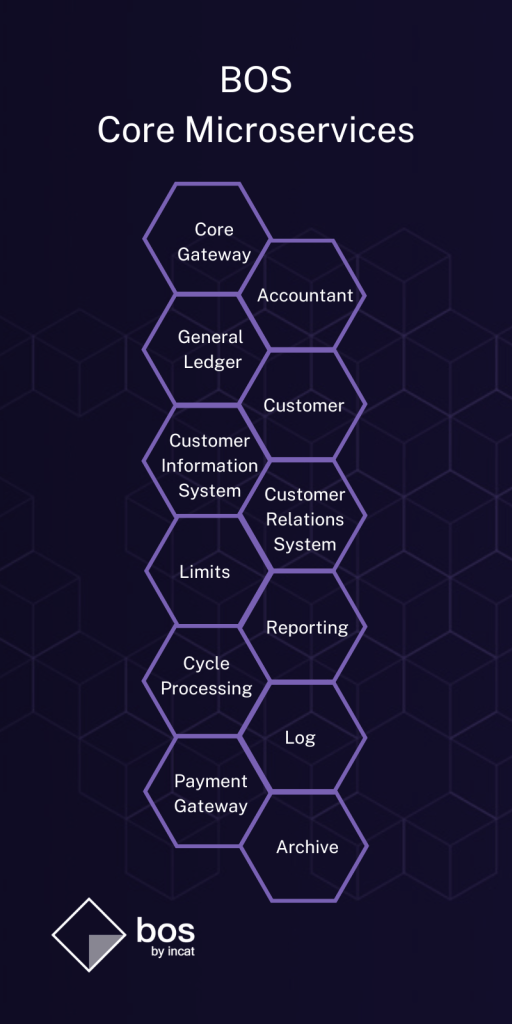
One of the examples of IT systems based on microservices is BOS – a transactional system dedicated for modern fintechs and digital banks. The BOS system consists of tens of product microservices. The product microservice allows you to handle all phases of the product, starting from initiation, through product processing in the system, and ending with product closure. The rationale behind the choice of such an architecture for BOS was primarily business scalability (selection of expected business lines with the possibility of future expansion) and technological (performance).
The product microservice allows you to handle all phases of the product, starting from initiation, through product processing in the system, ending with product closure.
How does the idea of microservices relate to the banking system in practice?
Let's imagine a transaction. What is most important, apart from the security of its implementation, is the processing time. Many things are checked as the banking system processes transactions. Financial conditions ranging from available funds through various types of limits to exchange rates. The client is also important. Do we need detailed customer data to process transactions in the context of high performance requirements? No, basic identification and descriptive information is usually sufficient. Taking this into account, from the point of view of transactional processing, a well-prepared customer database containing only the necessary information, such as identification data or residence qualifier, is sufficient. Everything is done quickly and efficiently. But from the point of view of the marketing department, things look different. It is necessary to have extensive knowledge about the client, its history, documents, connections, etc. Other types of information are necessary from the point of view of the credit assessment department.
In practice, the scenarios given here involve several independent and completely different scaled databases and supporting applications. From a transaction engine focused on instant transaction processing, to a limits database, to replicated customer knowledge placed in another database containing hundreds of customer information, to an independent database storing data on interpenetrating relationships between individual customer records. This is what microservices provide.
Not only technically, completely differently tuned environments, but by separating individual applications from each other, the possibility of independent development on the CIS (Customer Information System), CRS (Customer Relationships System) or Core (Transactional engine) modules.
This loosely coupled architecture allows to easily introduce adapters with very narrow functionality, such as SEPA adapter or SWIFT adapter which are used to connect to payment networks, meeting their standards, MT and ISO 20022 respectively.
Microservices in finance
Other example... Financial institutions generally recognize the advantages of developing more contemporary systems, but what if they wish to explore a novel functionality that customers are beginning to request? How can they conduct real-world testing without the risk of disrupting a well-functioning system? This is where the concept of microservices comes into play. By conceptualizing each fundamental element as an independent microservice, institutions can effectively evaluate and incorporate new features. For instance, if there is a new feature related to payment processing, they can integrate a dedicated payment service capable of seamlessly exchanging data with existing applications. If the new feature necessitates Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance, they can introduce the corresponding service gradually, gradually constructing a novel feature, application, or even an entire organization, while ensuring seamless communication between all components.
What if the customers wish to explore a novel functionality that customers are beginning to request? How can they conduct real-world testing without the risk of disrupting a well-functioning system? This is where the concept of microservices comes into play.
Now let's see in which areas of financial activity, microservice architecture is particularly applicable.
![]() Fraud Detection:
Fraud Detection:
Financial institutions heavily rely on fraud detection systems to protect their customers and mitigate risks. Microservices architecture allows for the development of specialized microservices dedicated to fraud detection algorithms, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition. These microservices can work in tandem to analyze large volumes of data and identify potential fraudulent activities in real-time.
![]() Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Microservices architecture can enhance CRM systems in the financial sector. Each microservice can handle specific aspects of customer interactions, such as customer onboarding, personalized offers, transaction history, and customer support. This modular approach enables banks to deliver tailored services and experiences to their customers while maintaining a high level of scalability and flexibility.
![]() Risk Management:
Risk Management:
Microservices architecture can be utilized to develop risk management systems for financial institutions. Different microservices can be responsible for data collection, risk assessment, compliance monitoring, and reporting. This distributed architecture allows for better risk analysis, faster response times, and easier integration with external data sources or regulatory systems.
![]() Payment Processing:
Payment Processing:
Microservices architecture enables financial institutions to build robust and scalable payment processing systems. Each microservice can handle a specific aspect of the payment process, such as authentication, transaction validation, fraud detection, and settlement. This modular approach allows for flexibility and easier maintenance of the system.
Of course, microservices are not a cure-all. So far, there is no architecture that would be free of defects, and at the same time would be suitable for any type of application. It is no different with microservices.
If you are considering implementing a microservices architecture, the key question you should ask yourself is not "Do?", but "How?", because incorrect development of technical requirements and structure, or lack of thoughtful handling of traffic between servers, can ultimately do more harm than good. good. Neglecting these issues at the planning stage may result in throwing the baby out with the bathwater, and as a result, it will most likely turn out that the architecture, which was supposed to make many things easier, in fact gives sleepless nights to all interested parties. Then it is worth considering the support of a technical partner who has experience in creating solutions based on microservices. Thanks to this, you will avoid many difficulties related to implementation and at the same time you will be sure that you will have an efficient release and a system that can be modified flexibly to adapt to rapidly changing business requirements on an ongoing basis.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR:

Michał Mazur is the Chief Analyst at INCAT Sp. z o.o. - the provider of BOS Core banking system.
In his over 20-year career, he has been involved in financial and IT sector projects. He has extensive experience in project management, analysis, business development, system architecture, and quality assurance. Michał is a graduate of AGH University of Science and Technology.
Contact an author: michal.mazur@incat.com.pl
4 cutting-edge business models of fintech companies

The fintech sector is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world. The global fintech market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.58% between 2023 and 2026, with the market size expected to reach $305.7 billion by 2026. The fintech industry attracted $105 billion in investment in 2020, which is an increase of 31% from 2019. In comparison, the overall venture capital industry saw a decline of 9% in the same year. No wonder many people starting their adventure with a business look at the fintech sector as a kind of promised land. In the article below, we analyze the 4 most popular business models that are worth exploring when taking your first steps in the fintech industry.
Nr 1 Payment App
In the payments sector, fintech companies have disrupted traditional payment methods by offering faster, cheaper, and more convenient payment solutions. One business model that has emerged in this sector is the mobile payment app. Mobile payment apps allow users to transfer funds, pay bills, and make purchases from their smartphones. These apps allow users to make payments quickly and easily, often using just their mobile device. Payment apps have disrupted the traditional payment industry, which has long been dominated by banks and credit card companies. Payment apps are expected to continue to grow in popularity as more people move towards cashless transactions and digital payments.
To build a successful payment app, there are several key components that need to be considered. These include:
![]() User experience: The user experience is critical to the success of a payment app. Customers should be able to easily navigate the app, and complete transactions quickly and securely. The design and functionality of the app should be intuitive and user-friendly.
User experience: The user experience is critical to the success of a payment app. Customers should be able to easily navigate the app, and complete transactions quickly and securely. The design and functionality of the app should be intuitive and user-friendly.
![]() Security: Security is also a key consideration when building a payment app. Customers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is secure. This requires robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection.
Security: Security is also a key consideration when building a payment app. Customers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is secure. This requires robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection.
![]() Payment options: A payment app should offer a variety of payment options, including credit and debit cards, bank transfers, and mobile wallets. This allows customers to choose the payment method that best suits their needs.
Payment options: A payment app should offer a variety of payment options, including credit and debit cards, bank transfers, and mobile wallets. This allows customers to choose the payment method that best suits their needs.
![]() Integration with other services: To provide a seamless experience for customers, a payment app should integrate with other financial services, such as budgeting apps and investment platforms. This allows customers to access all of their financial information and services in one place.
Integration with other services: To provide a seamless experience for customers, a payment app should integrate with other financial services, such as budgeting apps and investment platforms. This allows customers to access all of their financial information and services in one place.
Building a successful payment app requires a focus on user experience, security, payment options, integration with other services, and loyalty programs. By prioritizing these components, fintech companies can create payment apps that meet the needs and expectations of today's consumers.
Payment apps have disrupted the traditional payment industry, which has long been dominated by banks and credit card companies.
The payment app that is gaining more and more popularity in Europe is operating under the license of a Lithuanian bank ZEN. The main engine on which ZEN is based is BOS Core banking system. ZEN is a mobile application that offers a seamless and secure way for users to manage their digital assets. The app allows users to buy, sell, and store cryptocurrencies, as well as traditional currencies, all in one place. What sets ZEN apart is its user-friendly interface, fast and reliable execution of trades, and top-notch security features such as two-factor authentication and biometric login. With its global reach and innovative features, ZEN is poised to be a major player in the rapidly evolving world of digital finance.
Nr 2 - P2P lending platform
Another business model that has emerged in fintech is the peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platform. P2P lending allows borrowers to access loans directly from individual investors, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This model has disrupted the traditional lending industry, which has long been dominated by banks and other financial institutions.
P2P lending platforms have gained traction over the last decade due to their ability to offer lower interest rates to borrowers and higher returns to investors than traditional banks. They achieve this by cutting out the middleman, i.e., banks, and connecting borrowers directly with investors. This results in lower operational costs and higher profits for investors, which in turn translates into lower interest rates for borrowers.
P2P lending allows borrowers to access loans directly from individual investors, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This model has disrupted the traditional lending industry, which has long been dominated by banks and other financial institutions.
Moreover, P2P lending platforms use technology to streamline the lending process, making it faster and more efficient. Borrowers can apply for loans online, and investors can browse through loan applications and choose which ones to invest in. This approach provides greater transparency and control to both parties, which is a significant advantage over traditional lending models.
P2P lending platforms are not only disrupting the lending industry but are also attracting significant investments from venture capitalists and private equity firms. According to a report by PwC, the P2P lending market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.5% between 2020 and 2027, reaching a market size of $1,291.2 billion by 2027.
The popularity of these platforms can be attributed to several factors, including:
![]() Lower interest rates - P2P lending platforms offer borrowers lower interest rates compared to traditional banks, making loans more affordable and accessible.
Lower interest rates - P2P lending platforms offer borrowers lower interest rates compared to traditional banks, making loans more affordable and accessible.
![]() Faster loan approvals - P2P lending platforms use technology to streamline the loan application process, providing faster loan approvals and disbursements.
Faster loan approvals - P2P lending platforms use technology to streamline the loan application process, providing faster loan approvals and disbursements.
![]() Diversified loan portfolios - P2P lending platforms offer investors a range of investment opportunities, allowing them to diversify their portfolios and reduce their overall risk.
Diversified loan portfolios - P2P lending platforms offer investors a range of investment opportunities, allowing them to diversify their portfolios and reduce their overall risk.
![]() High returns on investment - P2P lending platforms offer investors higher returns on their investments compared to traditional investment options like savings accounts or bonds.
High returns on investment - P2P lending platforms offer investors higher returns on their investments compared to traditional investment options like savings accounts or bonds.
![]() Transparency - P2P lending platforms provide greater transparency to both borrowers and investors, with easy-to-use online platforms and detailed loan and investment information.
Transparency - P2P lending platforms provide greater transparency to both borrowers and investors, with easy-to-use online platforms and detailed loan and investment information.
One of the best known P2P platform is, founded in 2010 in the UK, Funding Circle. Funding Circle is one of the largest P2P lending platforms in the world, with over £11 billion in loans facilitated. The platform's popularity is due to its easy-to-use online application process, fast loan approvals, and competitive interest rates.
Despite the significant growth potential of P2P lending platforms, they also face challenges. One of the most significant challenges is managing credit risk. P2P lending platforms have to ensure that borrowers are creditworthy and can repay the loans. To manage this risk, P2P lending platforms use various credit assessment tools, including credit scores and other data analytics.
Another challenge for P2P lending platforms is regulatory compliance. As P2P lending platforms are relatively new, regulators are still developing the regulatory framework to govern them. This has resulted in a lack of clarity in some areas, which can make it challenging for P2P lending platforms to operate in a compliant manner.
Nr 3 - Digital banking
One of the most significant areas where fintech has been applied is in banking. Traditional banking has been challenged by fintech companies that offer innovative and customer-centric solutions. One example of such a business model is the digital-only bank. With the development of technology, consumers now expect seamless and convenient banking experiences that can be accessed from anywhere, at any time. Digital banks, also known as neobanks, are financial institutions that operate entirely online, without any physical branches. They offer a range of banking services, such as checking and savings accounts, loans, and credit cards, all accessible through their mobile apps or websites.
Digital banks also tend to have lower overhead costs than traditional banks, which can translate into lower fees and more competitive interest rates for customers. Users usually choose such banks because of a few reasons:
![]() Convenience - Digital banks offer 24/7 access to banking services, making it easy for customers to manage their finances on-the-go.
Convenience - Digital banks offer 24/7 access to banking services, making it easy for customers to manage their finances on-the-go.
![]() Lower fees - Digital banks often have lower overhead costs than traditional banks, allowing them to offer lower fees and more competitive interest rates.
Lower fees - Digital banks often have lower overhead costs than traditional banks, allowing them to offer lower fees and more competitive interest rates.
![]() User-friendly interfaces - Digital banks typically offer sleek and user-friendly mobile apps, making it easy for customers to navigate their banking services.
User-friendly interfaces - Digital banks typically offer sleek and user-friendly mobile apps, making it easy for customers to navigate their banking services.
![]() Personalization - Digital banks use data analytics to offer personalized banking services and recommendations to customers, allowing them to better manage their finances.
Personalization - Digital banks use data analytics to offer personalized banking services and recommendations to customers, allowing them to better manage their finances.
P2P lending allows borrowers to access loans directly from individual investors, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This model has disrupted the traditional lending industry, which has long been dominated by banks and other financial institutions.
If you want to seriously think about setting up a digital bank, consider in particular:
![]() User experience: The user experience is critical to the success of a digital bank. Customers should be able to easily navigate the bank's website and mobile app, and find the information they need quickly and easily. The design and functionality of the digital platform should be intuitive and user-friendly.
User experience: The user experience is critical to the success of a digital bank. Customers should be able to easily navigate the bank's website and mobile app, and find the information they need quickly and easily. The design and functionality of the digital platform should be intuitive and user-friendly.
![]() Security: Security is also a key consideration when building a digital bank. Customers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is secure. This requires robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection.
Security: Security is also a key consideration when building a digital bank. Customers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is secure. This requires robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection.
![]() Customer support: Despite the convenience of digital banking, customers still need to be able to get help when they have questions or issues. A digital bank should have a customer support team that is easily accessible through multiple channels, such as phone, email, and chat.
Customer support: Despite the convenience of digital banking, customers still need to be able to get help when they have questions or issues. A digital bank should have a customer support team that is easily accessible through multiple channels, such as phone, email, and chat.
![]() Integration with other services: To provide a seamless experience for customers, a digital bank should integrate with other financial services, such as payment platforms and investment apps. This allows customers to access all of their financial information and services in one place.
Integration with other services: To provide a seamless experience for customers, a digital bank should integrate with other financial services, such as payment platforms and investment apps. This allows customers to access all of their financial information and services in one place.
![]() Innovative features: Finally, a digital bank should offer innovative features that set it apart from traditional banks. This could include features such as real-time alerts, personalized financial advice, and gamification elements to encourage customers to save money.
Innovative features: Finally, a digital bank should offer innovative features that set it apart from traditional banks. This could include features such as real-time alerts, personalized financial advice, and gamification elements to encourage customers to save money.
One example of such a digital bank is based on the core banking system BOS - D360 bank. D360 is a new digital bank that has been approved by the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) and has become the third digital bank in Saudi Arabia to be licensed. The bank is being built by Derayah Financial Company, a leader in digital retail investments in Saudi Arabia. The main investor in D360 is the Public Investment Fund (PIF), a Saudi Arabian sovereign wealth fund known for its spectacular investments made in partnership with Softbank, such as in the shares of Uber.
Nr 4 UBI
In the insurance sector, fintech companies have introduced innovative solutions to simplify the insurance process and offer personalized policies to customers. One example of such a business model is the usage-based insurance (UBI) model. The usage-based insurance (UBI) model is a type of auto insurance that allows policyholders to pay premiums based on their driving behavior. With the rise of telematics technology and IoT devices, UBI has become an increasingly popular business model for fintech companies looking to disrupt the traditional auto insurance industry.
And why is this model so popular among users in the market? there are at least a few reasons
![]() Personalization - UBI allows insurance providers to offer personalized insurance rates based on a customer's driving habits, which can lead to lower premiums for safe drivers.
Personalization - UBI allows insurance providers to offer personalized insurance rates based on a customer's driving habits, which can lead to lower premiums for safe drivers.
![]() Cost savings - By offering lower rates to safe drivers, UBI can help customers save money on their auto insurance premiums.
Cost savings - By offering lower rates to safe drivers, UBI can help customers save money on their auto insurance premiums.
![]() Improved safety - UBI can incentivize safe driving practices and encourage drivers to be more aware of their driving behavior, ultimately leading to fewer accidents and safer roads.
Improved safety - UBI can incentivize safe driving practices and encourage drivers to be more aware of their driving behavior, ultimately leading to fewer accidents and safer roads.
![]() Transparency - UBI provides customers with detailed information about their driving behavior, allowing them to better understand their risk level and make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
Transparency - UBI provides customers with detailed information about their driving behavior, allowing them to better understand their risk level and make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
To build a successful UBI business, there are several key components that need to be considered. These include:
![]() Telematics technology: UBI relies on telematics technology to collect data on driver behavior. Telematics devices can be installed in vehicles to track factors such as speed, acceleration, braking, and distance traveled. Alternatively, data can be collected through mobile apps or connected car services.
Telematics technology: UBI relies on telematics technology to collect data on driver behavior. Telematics devices can be installed in vehicles to track factors such as speed, acceleration, braking, and distance traveled. Alternatively, data can be collected through mobile apps or connected car services.
![]() Data analytics: UBI companies use data analytics to gain insights into driver behavior and risk profiles. This data can be used to personalize insurance policies, set premiums, and incentivize safe driving.
Data analytics: UBI companies use data analytics to gain insights into driver behavior and risk profiles. This data can be used to personalize insurance policies, set premiums, and incentivize safe driving.
![]() Personalization: UBI policies are tailored to each individual policyholder based on their driving behavior. This can lead to lower premiums for safe drivers and higher premiums for high-risk drivers.
Personalization: UBI policies are tailored to each individual policyholder based on their driving behavior. This can lead to lower premiums for safe drivers and higher premiums for high-risk drivers.
![]() Customer engagement: UBI companies need to engage with customers to promote safe driving behavior and incentivize policyholder retention. This can be done through gamification, rewards programs, and personalized coaching.
Customer engagement: UBI companies need to engage with customers to promote safe driving behavior and incentivize policyholder retention. This can be done through gamification, rewards programs, and personalized coaching.
![]() Regulatory compliance: UBI companies need to comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards. This includes obtaining appropriate licenses and registrations, and ensuring that customer data is protected and secure.
Regulatory compliance: UBI companies need to comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards. This includes obtaining appropriate licenses and registrations, and ensuring that customer data is protected and secure.
The UBI model offers a promising business model for fintech companies looking to enter the auto insurance industry. By leveraging telematics technology, data analytics, personalization, customer engagement, and regulatory compliance, UBI companies can create innovative new products and services that disrupt the traditional auto insurance industry and provide greater value to customers.
Fintech has disrupted various sectors by introducing innovative business models that offer more personalized and customer-centric solutions. Digital-only banks, P2P lending platforms, mobile payment apps, and UBI models are just a few examples of the many business models that have emerged within fintech. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more disruptive business models emerge in the future.
Breaking free from Cloud Lock-In: The Benefits of Cloud-Agnostic Core Banking Systems

The banking industry has evolved significantly in recent years, with the introduction of cloud-based systems enabling banks to improve their services, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of cloud-agnosticism, which is a key feature of BOS core banking system.
Cloud-agnosticism - what does it mean?
Many of the cloud-native or cloud-ready solutions are fully linked to the particular cloud technology suite. It brings a lot of advantages in a solution implementation, its installation and maintenance but in other hand such approach limit potential use of the solution to the chosen cloud and their tools. A cloud-agnostic system is a type of system that is designed to work on any (or almost any) cloud platform. In other words, it is a system that can run on multiple cloud platforms without requiring any crucial modifications to the system and the tools required for its installation, operation and monitoring. This contrasts with non-cloud-agnostic systems, which are designed and implemented to run on a specific cloud platform.
BOS equals flexibility
One of the main advantages of a cloud-agnostic system's nature is flexibility. This flexibility allows for greater resilience and avoids vendor lock-in. Users can easily switch between cloud platforms if they find a better fit for their business needs, without migrating their entire system. This can save time and resources and allow for greater agility in responding to business and technological requirements. It also allows financial institutions to integrate new technologies and services into their existing systems quickly, without requiring significant changes to their infrastructure or architecture.
Cloud-agnostic systems are also cost-effective compared to non-cloud-agnostic systems since they eliminate the need for banks to maintain their own infrastructure and hardware or paid public cloud tools. This results in significant cost savings for institutions, which they can pass on to their customers in the form of lower fees and better rates.
Users can easily switch between cloud platforms if they find a better fit for their business needs, without migrating their entire system.
Security matters
Cloud-agnostic systems can improve security for financial institutions, as they can choose the cloud platform that provides the best security features. This can help institutions protect their customers' data and prevent security breaches.
Cloud-agnostic systems can increase innovation for banks, as they can take advantage of the latest cloud technologies and features. This can help financial institutions stay ahead of the competition and provide better services to their customers.
Comparison of cloud- agnostic and non-cloud agnostic core systems
| Comparison | Cloud Agnostic System | Non-Cloud Agnostic System |
| A system that is designed to run on any cloud platform or infrastructure without being tied to any specific cloud provider. | A system that is designed to run on a specific cloud platform or infrastructure, making it difficult to switch to another platform. | |
| Highly flexible and adaptable, allowing the system to run on any cloud infrastructure, including public, private, or hybrid clouds. | Less flexible as it is designed to run on a specific cloud platform or infrastructure. | |
| No vendor lock-in as it is designed to be platform-agnostic and can be easily migrated to another cloud platform or infrastructure. | High risk of vendor lock-in as the system is designed to run on a specific cloud platform or infrastructure, making it difficult to switch to another platform. | |
| More cost-effective as the system can be easily implemented or migrated to a cloud platform or infrastructure that offers the best pricing and performance. | Less cost-effective as the system is tied to a specific cloud platform or infrastructure, limiting the options for pricing and performance optimization. | |
| Highly scalable as it can be easily scaled up or down depending on the changing business needs and workload demands. | Limited scalability as it is tied to a specific cloud platform or infrastructure, making it difficult to scale up or down to meet changing business needs and workload demands. | |
| Highly resilient as it can be easily replicated across multiple cloud platforms or infrastructures, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery. | Less resilient as it is tied to a specific cloud platform or infrastructure, increasing the risk of service disruption and downtime in case of a cloud outage or disaster. | |
| The ability to choose tools supporting the operation of cloud systems that allow for their optimal use in the organization of financial institutions or the capabilities of the provider of technical operations services | Limited to the possibilities offered by native solutions of a specific cloud |
Cloud-agnostic banking systems provide several advantages over non-cloud-agnostic systems, including increased flexibility and scalability, reduced costs, improved security, and unlimited innovation.
BOS is a perfect example of a cloud-agnostic banking system that provides these advantages, making it an attractive option for banks looking to improve their digital capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that more banks will move towards cloud-agnostic systems in order to stay competitive in the market.
***
If you want to transform your business idea into a financial masterpiece and need help in implementing a core system for your activity, contact us.
Event-Driven Core Banking: a deep look into BOS architecture

This is the first article from the "BOS Inside" series in which we will introduce you to our system from the perspective of its architecture, functionality and main technological advantages.
Core banking systems are the backbone of financial institutions that enable them to manage their day-to-day operations efficiently. The system provides functionality that ranges from opening and managing accounts to processing payments, managing deposits, creating loan accounts and calculating interest rates. In recent years, the financial industry has seen a shift towards event-driven architectures that allow for better scalability, flexibility, and faster time-to-market. One example of a core banking system that utilizes event-driven architecture is the BOS system provided by INCAT.
What is event-driven architecture?
Event-driven architecture is a communication model where the system reacts to an event rather than relying on traditional request-response interactions. Events can be anything from a user interaction to changes in the state of the system or external data source. By using an event-driven architecture, core banking systems can respond to these events in real-time, improving system performance, reducing latency, and increasing scalability.
The event-driven model allows for a loosely coupled and highly decoupled system that can adapt to changes in demand without significant modifications to the core system.
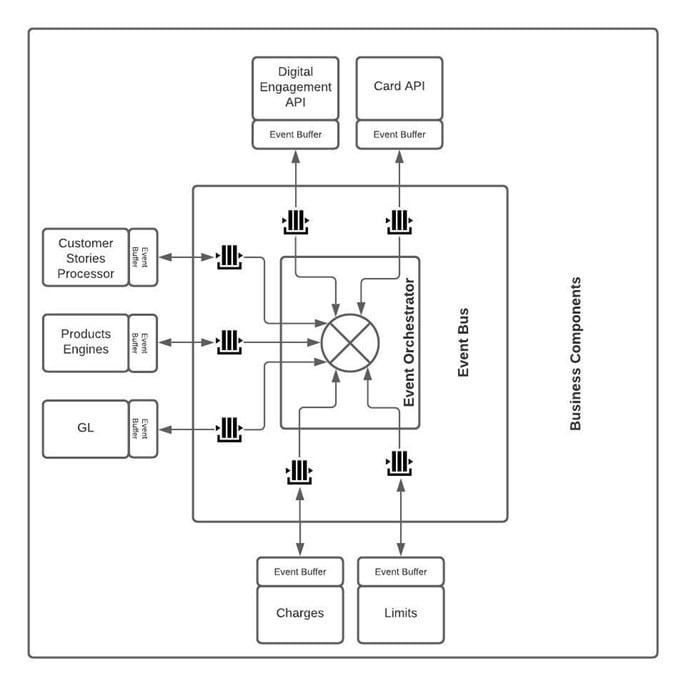
The main components of the event-driven architecture of the BOS system are:
![]() Event Orchestrator - a component that allows for the implementation of event distribution processes along with the definition of dependencies between generated events.
Event Orchestrator - a component that allows for the implementation of event distribution processes along with the definition of dependencies between generated events.
![]() Event Bus – a set of queues based on Kafka technologies, allowing for asynchronous exchange of messages.
Event Bus – a set of queues based on Kafka technologies, allowing for asynchronous exchange of messages.
![]() Event Buffer – a component built into business microservices that ensures the transactionality of message exchange and allows you to manage the business processing of events in the business microservice.
Event Buffer – a component built into business microservices that ensures the transactionality of message exchange and allows you to manage the business processing of events in the business microservice.
How BOS Uses Event-Driven Architecture?
BOS' event-driven nature allows for seamless integration with other systems and provides high flexibility and scalability. The system's communication model follows a publish-subscribe pattern, where events are published by producers and subscribed to by consumers. The publish-subscribe model allows for efficient and scalable communication between the system's components.
The BOS system has a robust event processing engine that can handle a high volume of events in real-time. The system's event processing engine uses an internal event bus that allows for the easy management and routing of events. The event bus allows the system to route events to the appropriate component and ensures that the events are processed in a timely manner. The event processing engine also allows for the filtering, transformation, and aggregation of events, providing a high degree of flexibility.
The system's event-driven approach allows for easy integration with third-party systems. The event-driven model enables easy data exchange and sharing between the system and other systems, providing a high degree of interoperability. In addition, the system's APIs also support easy integration with other solutions.
Where does BOS utilize event-driven architecture?
BOS rely on the event-driven architecture in various key areas, including:
![]() Account Management: to manage the opening and closing of accounts, updating account balances, and managing account status changes.
Account Management: to manage the opening and closing of accounts, updating account balances, and managing account status changes.
![]() Transaction Management: to manage transactions, including the initiation, processing, and settlement of transactions.
Transaction Management: to manage transactions, including the initiation, processing, and settlement of transactions.
![]() Customer Management: to manage customer-related activities, including customer onboarding, account access management, and customer data updates.
Customer Management: to manage customer-related activities, including customer onboarding, account access management, and customer data updates.
Benefits of BOS’ event-driven architecture
One of the key advantages of BOS’ event-driven architecture is its ability to handle complex and dynamic data flows. In a traditional architecture, data flow is managed through a central controller, which can quickly become a bottleneck as data volumes increase. With an event-driven architecture, data flow is managed through a distributed network of modules, which can handle data volumes more efficiently and scale dynamically as the system grows.
Another feature of BOS’ even driven nature is its ability to enable real-time data processing and analysis. With traditional architectures, data processing is often batch-based, which means that data is processed in batches at predetermined intervals. This approach can lead to delays in data processing and analysis, which can impact the overall efficiency of the system. With the event-driven architecture, data processing is performed in real-time, enabling financial organizations to make the right decisions based on up-to-date information.
In addition to its advanced architecture, the BOS Core Banking System also offers a comprehensive set of features and modules. This approach enables banks to build a system that is tailored to their business requirements, which can help them to operate more efficiently and effectively.
In conclusion, the adoption of event-driven architecture in core banking systems is a significant development in the banking industry. With its advanced architecture and modular design, the BOS core banking system is well positioned to help banks and fintechs in the digital age.
BNPL 2023 predictions

Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) deferred service has been growing rapidly for over 3 years. However, despite this rapid growth, market experts believe that in the face of rising interest rates and expensive money, consumers' potential for excessive indebtedness will decrease. This, in turn, means that the current BNPL model will have to change. In which direction can the service evolve? We have analyzed several probable directions.
![]() What is BNPL?
What is BNPL?
BNPL is a service that allows customers to make purchases and then defer payment for 30 or even 45 days. It is a type of installment loan that typically allows you to purchase something immediately with little or no initial payment and pay off the balance over four or fewer payments. BNPL also promotes better budget planning.
![]() The increasing popularity of BNPL in e-commerce
The increasing popularity of BNPL in e-commerce
E-commerce is currently one of the fastest-growing sectors of the economy worldwide. In such a dynamic industry, BNPL is a powerful sales booster - it doesn’t only increase the number of customers and revenues, but also promotes customer loyalty. Additionally, BNPL is increasingly used in e-commerce for follow-up abandoned carts to encourage customers to complete their purchases. Most of the European sellers and marketplace platforms are considering (or have already introduced) their own BNPL solutions. Such a service is already offered e.g. by the leader of the Polish e-commerce platform Allegro, as well as by Amazon, which offers a BNPL service for selected products and suppliers.
![]() Expansion of product range
Expansion of product range
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) services have seen significant success in the past few years, especially in the areas of apparel, electronics, and appliances. It is predicted that in 2023, this trend will continue, but new product categories will be covered by this form of funding. We can expect BNPL to be offered in the furniture, automotive, and real estate sectors. There will probably show up "rent to own" options allowing customers to rent the product for a specific time, after which they can purchase it. BNPL is also likely to appear in the travel industry. A couple of months ago, Afterpay - an Australian BNPL operator, announced a partnership with Expedia, which specializes in online travel purchases for individual customers and small businesses. As part of the collaboration, customers received the option to pay for trips worth up to 2000 dollars in installments. According to the company's representatives, in the next few years, travel will become one of the most frequently financed expenditures through BNPL by consumers.
According to Afterpay, in the next few years, travel will become one of the most frequently financed expenditures through BNPL by consumers.
![]() BNPL as a credit card alternative
BNPL as a credit card alternative
The BNPL service is becoming increasingly seen as an alternative to credit cards, especially now - as consumers feel the effects of inflation and many are in a worse financial situation than a year or two ago. More and more consumers are choosing BNPL, as it is more flexible and allows for greater control over expenses. In a survey conducted by The Ascent, 62% of respondents expressed the belief that "BNPL is a solution that will completely replace the credit card in the future." Similar conclusions can be drawn from analyzing the results of a survey conducted by the Insider Intelligence service. On the question of reasons for using deferred payments, 39.4% (the dominant percentage) of respondents indicated they "wanted to avoid paying with a credit card." In addition, one - sixth of the survey participants chose BNPL because "they don't like using credit cards."
![]() Mergers and Acquisitions in the BNPL Industry
Mergers and Acquisitions in the BNPL Industry
The rapid development of BNPL has attracted many new players offering the service to the market, including banks that are introducing their own "Buy Now Pay Later" versions and start-ups trying to offer deferred payments in various niche sectors. However, the main international market players, such as Klarna, Affirm and ZIP, are still striving for profitability. As part of these efforts, they are making acquisitions and transitions, including the acquisition of Square Inc. by ZestFinance and the acquisition of Behalf by Klarna. Any analysis of the development of the BNPL industry indicates that this trend will also continue in the current year.
The increased governement's control over BNPL services may help sellers avoid potential allegations of unfair practices.
![]() Regulatory Oversight of BNPL
Regulatory Oversight of BNPL
As BNPL is seen as a close substitute for credit cards, regulators are paying more and more attention to deferred payment services. According to a report published by PwC, many countries are now considering regulations on BNPL to protect consumers from excessive debt. Governments around the world are particularly concerned that, since BNPL payments are largely used mainly by young users, they may not be prepared for later repayment of their debts. As the BNPL sector continues to rapidly develop, it is more likely than ever that regulations and controls will increase. However, this may be good news for sellers, as increased control over services may help sellers avoid potential allegations of unfair practices.
***
If you are looking for tools to create your own BNPL solution, please contact us.
8 most popular programming languages used in banking/finance

If you were to ask groups of programmers what technology is best for creating software for banking, the answer would undoubtedly be "It depends." And it's hard to disagree, as the choice of technology depends on the goal that it is supposed to achieve. However, taking into account the specificity of the banking industry, stringent security standards and the need for compliance with legislation, we have chosen 8 technologies that are most commonly used in banking and finance sector.
![]() COBOL
COBOL
COBOL is a legacy language that has been used for many years as the foundation of banking systems. Anyone who has had at least a moment of contact with this subject associates it as the long-standing basis of all banking systems. Although today programmers sometimes joke about this language, it turns out that it is not deserved. According to Reuters data, as much as 43% of today's global banking IT systems are created using COBOL, so as you can see, it still has quite a good reputation. The name COBOL is an acronym for Common Business-Oriented Language, and the fact that it is excellent at achieving business and commercial goals is what largely explains its use in banking. In addition, COBOL is also characterized by simple and understandable syntax, which makes it easy even for a non-technical person to understand while reading the code.
According to Reuters, 43% of today's global banking IT systems are created using COBOL.
![]() C#
C#
C# is a high-level object-oriented language created by Microsoft. It is known for its ability to create complex systems and large projects. Despite the passage of time, it still occupies high positions in popularity rankings of programming languages. It works great for creating advanced systems and large projects, which partly explains its place in this article. What sets C# apart is primarily the fact that it is a technology from the Microsoft stable, which has at least two major advantages. The first is, of course, the fact that this language is behind one of the technological giants, with a huge budget for development and a lot of support. The second is undoubtedly a high level of backward compatibility (a feature of software that allows the new version to work with the entire environment of the previous version and all its components). In the context of such desirable predictability, Microsoft openly defines the direction of development of its technology, so it can be quite clearly and clearly predicted what changes we will have to face in the next few years.
![]() C/C++
C/C++
Although C/C++ was created in the 1980s, its wide range of applications means that many large systems and applications still rely on it. C++ stands out for its ability to create complex, multi-level systems due to its specific compiler. The C++ compiler strongly enforces type compliance, making it harder to make errors in the code written in C++, leading to greater security of applications written in this language. C++ is also used in the fintech industry, known for its efficiency, tight data structures and template metaprogramming, making it one of the fastest programming languages
![]() JAVA/ SPRING
JAVA/ SPRING
Java is the undisputed king of banking technologies that needs no introduction. It works great in projects that require a very high level of security and high performance. It is also characterized by high stability and is often used in large implementations. What sets Java apart is its independence from the architecture, meaning it can run on any system. The created code is independent of the operating system and processor, and is executed by the so-called Java Virtual Machine, which (among other things) translates universal code into code adapted to the specifics of a particular operating system and processor. Such universality means that everywhere where it is possible to install a virtual machine, it is also possible to use Java. BOS core banking system has been written in the JAVA language, and it has been implemented on Kubernetes container.
![]() JAVASCRIPT/ ANGULAR.JS
JAVASCRIPT/ ANGULAR.JS
JavaScript, or rather the framework of this language, Angular.js, is the most commonly chosen technology when creating the front-end layer of banking applications. JavaScript allows building web applications in SPA (Single Page Application) technology, which greatly facilitates intuitive use of the application. Like other languages, JavaScript is a very stable language, supported for many years. Given that front-end technologies are changing almost daily and there is a large gap among them, in terms of stability and predictability, JavaScript seems to be the most optimal choice.
![]() PYTHON
PYTHON
Python is a technology that is most commonly used in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as in data analysis and data science. It is a language of very wide application, and given that banks are increasingly using AI algorithms, it is not surprising that Python's popularity in this industry is growing. Python is friendly to mathematics, and therefore well "understands" financial algorithms. Interestingly, many fintech and core banking organizations often use Python for data analysis, and given the growing need for technological cooperation between the banking industry and other quasi-financial institutions, one can expect its popularity in this area to increase. Popular banks such as Credit Suisse and Barclays are particularly interested in Java and Python skills.
![]() GO
GO
Go is a relatively new programming language that is gaining popularity in the banking industry due to its ability to handle large amounts of data and its ease of use. It is often used for developing applications that require high performance and scalability.
![]() RUST
RUST
Rust is a systems programming language that is gaining traction in the banking industry for its focus on security and memory safety. It is used for developing low-level systems and applications that require high performance and security.
What is very significant in the case of banking technologies is the fact that for creating software and individual components, languages that have been long supported and relatively predictable are usually chosen. Since banking systems are complex and extensive, banks rarely decide to rewrite them from one technology to another. Therefore, stability and the guarantee that the language will be supported for as long as possible, often at the expense of technological development in the industry, are crucial. What will certainly be one of the challenges for banking in the coming years is to find a compromise between using proven solutions, security and stability, and the ability to develop and use the latest technologies.
7 tech trends in 2023

No-code and low-code, AI and machine learning, 5G, or the development of cybersecurity solutions. According to BOS analysts, it is these trends that will shape the reality of many tech companies in the coming months of 2023.
While it is quite difficult to predict precisely what new technologies will emerge in the coming year in these uncertain and at the same time highly dynamic years, there are several key technological developments that are likely to continue and potentially accelerate in 2023.
So what turn of events should we expect?
Digitization first
The main conclusion from the analysis prepared by our team is that IT leaders must focus primarily on further accelerating digital transformation and consider the possible use of both technologies that can be used immediately and those that are on the horizon.
With this as a background, the top 7 strategic tech trends for 2023 are as follows:
![]() Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning have already begun to revolutionize many industries and will likely continue to do so in the coming year. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, have the ability to analyze and interpret large amounts of data, allowing them to perform tasks that would be difficult or impossible for humans to do. In 2023, we can expect to see the development and deployment of even more advanced and sophisticated AI systems in a variety of settings, including self-driving cars, intelligent personal assistants, and advanced analytics. The potential applications for AI are vast and varied, and it is likely that we will continue to see significant progress in this area in the coming year.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning have already begun to revolutionize many industries and will likely continue to do so in the coming year. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, have the ability to analyze and interpret large amounts of data, allowing them to perform tasks that would be difficult or impossible for humans to do. In 2023, we can expect to see the development and deployment of even more advanced and sophisticated AI systems in a variety of settings, including self-driving cars, intelligent personal assistants, and advanced analytics. The potential applications for AI are vast and varied, and it is likely that we will continue to see significant progress in this area in the coming year.
In the coming year, we may witness the development and implementation of even more advanced and sophisticated AI systems in a variety of settings.
![]() The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to be a significant tech trend in 2023, as it continues to expand and become more integrated into our daily lives. The IoT refers to the network of connected devices that are able to communicate with one another and transmit data over the internet. These devices can include everything from smart home devices and wearable technology to industrial equipment and infrastructure. In 2023, we can expect to see even more devices becoming connected and able to share data, leading to greater efficiency and convenience in a variety of settings. The potential applications for the IoT are vast and varied, and it is likely that we will continue to see significant progress in this area in the coming year.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to be a significant tech trend in 2023, as it continues to expand and become more integrated into our daily lives. The IoT refers to the network of connected devices that are able to communicate with one another and transmit data over the internet. These devices can include everything from smart home devices and wearable technology to industrial equipment and infrastructure. In 2023, we can expect to see even more devices becoming connected and able to share data, leading to greater efficiency and convenience in a variety of settings. The potential applications for the IoT are vast and varied, and it is likely that we will continue to see significant progress in this area in the coming year.
![]() 5G technology is the next generation of wireless communication standards, and it is expected to significantly increase the speed and capacity of mobile networks. In 2023, we can expect to see more widespread deployment of 5G technology, which could potentially enable new applications and services that require high-bandwidth connectivity. This could include everything from streaming high-definition video and virtual reality experiences to advanced analytics and the Internet of Things. As 5G technology becomes more widespread, it is likely to have a significant impact on a variety of industries and applications.
5G technology is the next generation of wireless communication standards, and it is expected to significantly increase the speed and capacity of mobile networks. In 2023, we can expect to see more widespread deployment of 5G technology, which could potentially enable new applications and services that require high-bandwidth connectivity. This could include everything from streaming high-definition video and virtual reality experiences to advanced analytics and the Internet of Things. As 5G technology becomes more widespread, it is likely to have a significant impact on a variety of industries and applications.
![]() Virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) technologies have the potential to change the way we interact with the world around us, allowing us to experience immersive, digital environments and overlaying digital information on top of the physical world. In 2023, we may see more widespread adoption of VR and AR technologies in a variety of settings, including gaming, education, and training. As these technologies continue to advance and become more sophisticated, they are likely to have a significant impact on a variety of industries and applications.
Virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) technologies have the potential to change the way we interact with the world around us, allowing us to experience immersive, digital environments and overlaying digital information on top of the physical world. In 2023, we may see more widespread adoption of VR and AR technologies in a variety of settings, including gaming, education, and training. As these technologies continue to advance and become more sophisticated, they are likely to have a significant impact on a variety of industries and applications.
![]() Blockchain technology which powers cryptocurrencies is a distributed ledger technology that allows for secure and transparent record-keeping without the need for a central authority. In 2023, we may see more widespread adoption of blockchain technology in a variety of industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. As technology continues to mature and be adopted by more organizations, it is likely to have a significant impact on the way we transact and exchange value.
Blockchain technology which powers cryptocurrencies is a distributed ledger technology that allows for secure and transparent record-keeping without the need for a central authority. In 2023, we may see more widespread adoption of blockchain technology in a variety of industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. As technology continues to mature and be adopted by more organizations, it is likely to have a significant impact on the way we transact and exchange value.
![]() No-code and low-code platforms are expected to be significant tech trends in 2023, as they continue to gain popularity and become more widely adopted. No-code and low-code platforms allow users to build software and applications without writing traditional code, using visual programming interfaces and pre-built modules. This can significantly reduce the time and resources required to develop and deploy software, making it possible for a wider range of individuals and organizations to create custom solutions. In 2023, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of no-code and low-code platforms, particularly as more organizations look to rapidly develop and deploy custom digital solutions. As these platforms continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, they are likely to have a significant impact on the way software is developed and deployed.
No-code and low-code platforms are expected to be significant tech trends in 2023, as they continue to gain popularity and become more widely adopted. No-code and low-code platforms allow users to build software and applications without writing traditional code, using visual programming interfaces and pre-built modules. This can significantly reduce the time and resources required to develop and deploy software, making it possible for a wider range of individuals and organizations to create custom solutions. In 2023, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of no-code and low-code platforms, particularly as more organizations look to rapidly develop and deploy custom digital solutions. As these platforms continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, they are likely to have a significant impact on the way software is developed and deployed.
![]() Cybersecurity. The development of solutions dedicated to cyber security is perceived as one of the biggest challenges for IT department managers in 2023, as the threat of cyber-attacks continues to grow and evolve. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the proliferation of connected devices, it is more important than ever to ensure the security of online systems and data. In 2023, we can expect to see continued development and deployment of cybersecurity technologies and practices, including advanced security analytics, artificial intelligence-based threat detection, and secure software development practices. As cyber-attacks become more sophisticated and targeted, it is crucial that organizations and individuals remain vigilant and take steps to protect themselves from these threats.
Cybersecurity. The development of solutions dedicated to cyber security is perceived as one of the biggest challenges for IT department managers in 2023, as the threat of cyber-attacks continues to grow and evolve. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the proliferation of connected devices, it is more important than ever to ensure the security of online systems and data. In 2023, we can expect to see continued development and deployment of cybersecurity technologies and practices, including advanced security analytics, artificial intelligence-based threat detection, and secure software development practices. As cyber-attacks become more sophisticated and targeted, it is crucial that organizations and individuals remain vigilant and take steps to protect themselves from these threats.
Cybersecurity became crucial at the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic when most companies switched to remote work and began to widely use cloud solutions. With the dynamic development of these services, as well as the introduction of the 5G network, IT security in 2023 will certainly not be forgotten.
Great certainty or great unknown?
In conclusion, 2023 is shaping up to be an exciting year for technology and innovation. From artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things to 5G, virtual and augmented reality, blockchain, cybersecurity, and no-code and low-code platforms, there are many trends that are likely to shape the development and adoption of new technologies in the coming year. It is difficult to predict exactly what new technologies will emerge in 2023, but it is clear that these and other trends will continue to shape the future of technology and have a significant impact on a variety of industries and applications. As we move into the new year, it will be interesting to see how these trends continue to evolve and what new technologies emerge on the horizon.
Core banking software for fintech start-ups. How to choose it the right way?

Fintech is currently one of the fastest-growing sectors in the world. According to the statistics, by 2026, the global financial technology market value is expected to reach 324 billion U.S. dollars. Additionally, fintech organizations are currently responsible for 30% of technology investments globally. All this means that new fintech solutions related to payments or lending, and more recently other areas of finance such as cryptocurrencies or insurance, are entering the market in large numbers.
As a financial start-up, choosing the right software is crucial for your business. The right software can help you manage your operations efficiently, improve your customer service, and stay compliant with industry regulations. One of the key pieces of software you'll need is a core banking system.
Core banking system - what is it?
This is a comprehensive, integrated software system that enables you to manage your core banking functions, such as processing transactions, opening new accounts, managing cards’ transactions, processing payments, maintaining customer records, and providing access to banking services. Many core banking systems are now cloud-based, which means you can access them from any device with an internet connection.
These systems offer multiple advantages, including streamlining financial processes, keeping pace with fast-evolving markets, providing convenience to customers, and extending digital reach to remote locations. Essentially, the core banking system is designed to support existing and potential customers with greater freedom in disposing their funds and support their plans of goods purchasing.
The most modern core banking systems are those referred to as “cloud-native”. What does it exactly mean and what kind of benefits does it give the user?
Born in the cloud
The cloud-native core banking model is essentially a suite of digital and processing financial solutions all stored on the cloud. The biggest benefits of cloud-native software are:
![]() Resilience
Resilience
Being supported by microservices architecture provides a significant advantage to those who use cloud solutions. That’s because it permits the load to be smoothly distributed on services, a geo-distributed architecture to be developed, and the distribution of service resources to be tightly controlled.
![]() Reduced Costs
Reduced Costs
When the switch is made to a cloud solution, it negates the need for expensive on-site infrastructure, as well as costly maintenance, storage and security updates.
![]() Increased Speed of Operation
Increased Speed of Operation
A number of elements, such as storage, data capture and interpretation processes, can be centralized using cloud technology. It’s also able to bring down the costs associated with these vital processes and result in much more precise, richer and more rapid data-led insights that can be used to boost performance by financial institutions.
Which is the best core banking system?
When choosing software for your financial start-up, there are a few key factors to consider.
![]() Easy integration
Easy integration
First, you'll want to choose software that is easy to use and integrate with your existing systems. This will help you get up and running quickly and minimize disruption to your business.
![]() Flexibility and scalability
Flexibility and scalability
Second, you'll want to choose software that is scalable, so that it can grow with your business. This is particularly important for financial start-ups, which often experience rapid growth in the early stages of their development.
![]() Compliant with industry regulations
Compliant with industry regulations
Third, you'll want to choose software that is secure and compliant with industry regulations. This is essential to protect your customers' data and ensure that your business stays on the right side of the law. for your business. The right software can help you manage your operations efficiently, improve your customer service, and stay compliant with industry regulations.
"The right software can help you manage your operations efficiently, improve your customer service, and stay compliant with industry regulations."
What is the Core Banking example?
Core Banking products are designed to process and manage different functions of different types of financial institutions. Examples of core banking products include e.g. Thought Machine, Transact by Temenos, Mambu or BOS by INCAT.
Transact by Temenos is well known as software for licensed and traditional banks, and Mambu and Thought Machine provide their software that is mostly focused on large-scale fintech projects and digital banks, whereas BOS serves mostly small and medium-sized companies with limited budgets.
For small and medium-sized fintech projects
BOS – the Banking Operation System is a fully scalable, cloud native & agnostic, modern transaction system that relies on microservices. BOS enables fast execution and integration of the system with external systems. The in-built components of integration (APIs) allow you to implement BOS easily and effectively and incorporate it with your financial organization. That lets you deploy the mature product and launch it onto the market soon. Furthermore, BOS supports the company by providing instant responses to the fluctuating market and customer expectations.
The system structure will enable smooth modification of its separate components to promise effective working of your product. In addition to this, the data supplied from the systems integrated into your business and other processes would be easier to manage for your organization.
The top and stand-out features of BOS that promise business growth are:
![]() Microservices architecture
Microservices architecture
![]() Event manager
Event manager
![]() Cloud-native & cloud-agnostic
Cloud-native & cloud-agnostic
![]() Data base agnostic
Data base agnostic
![]() Open API
Open API
![]() Multi-branding/ muti-institution
Multi-branding/ muti-institution
![]() Unique business functionalities
Unique business functionalities
![]() Integrated general ledger
Integrated general ledger
Overall, choosing the right software is crucial for the success of your financial start-up. By carefully considering your needs and doing your research, you can find the right tools to support your business and help it grow.
***
If you want to transform your business idea into a financial masterpiece and need help in implementing a basic system for your activity, contact us.